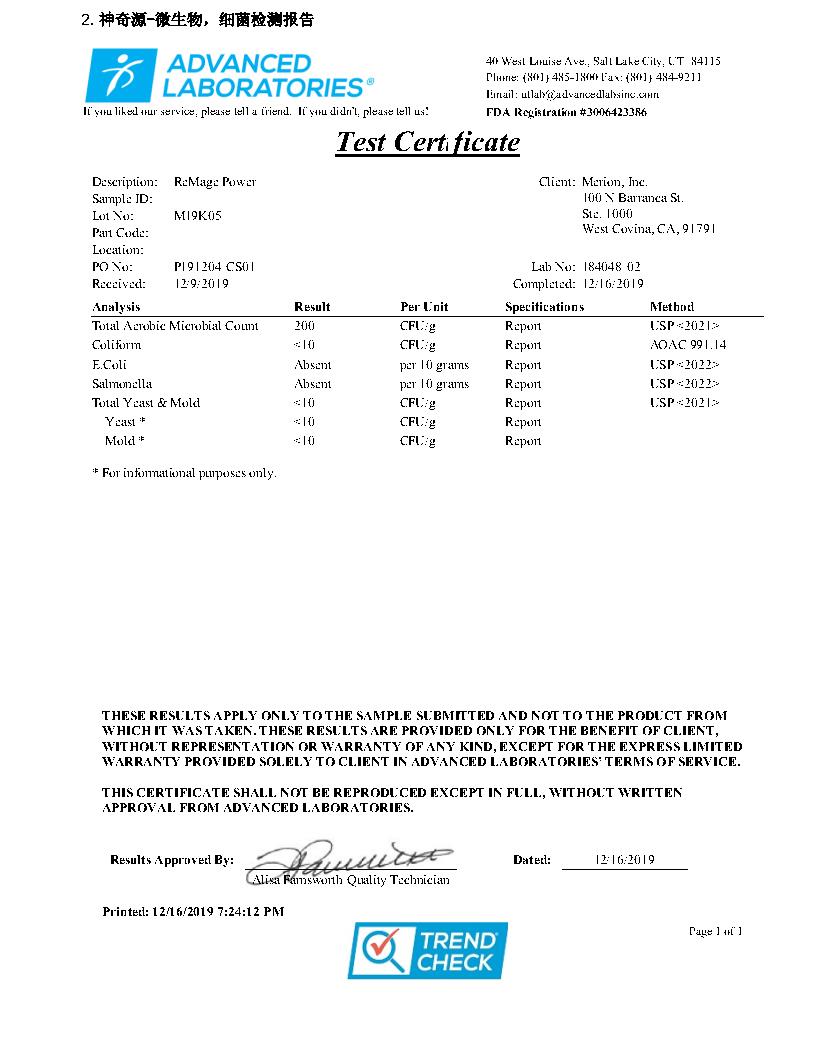
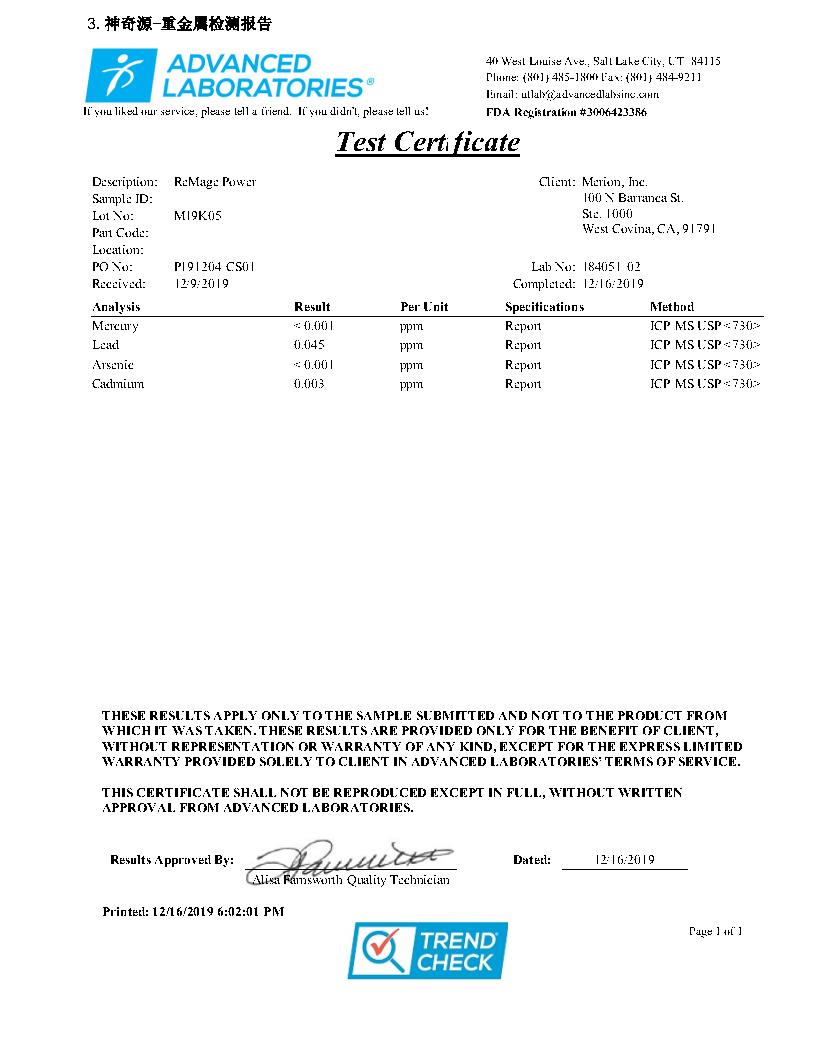
We Make Supplements For You !
ReMage-Power
ReMage-Power 600mg / 60Capsules Gold bottle
How to stay young?
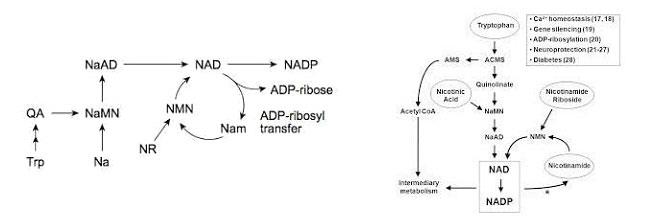
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), NMN plays an important role in human cell energy production, it is involved in the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).
ReMage Power
Anti-Aging NAD+ Support
Promotes Energy Metabolism
β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), NMN plays an important role in human cell energy production, it is involved in the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), and NAD+ is an important coenzyme for energy conversion.
Product description:
ReMage-Power contains β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide, NMN with high purity and high enzyme activity.
Among them, NMN is a nucleotide derived from ribose and nicotinamide, which is a naturally occurring compound that plays an important role in cellular energy metabolism. β-nicotinamide mononucleotide ("NMN") is involved in the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +). It is inactive by itself. It is not truly physiological until it is converted into NAD + in the human body.
NAD + full name nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, also known as Coenzyme I or Noga factor. It is involved in 200 kinds of redox enzyme reactions in the human body, the most important of which are the acetylases Sirtuin1-7 and type 1 poly ADP ribose polymerase PARP1. NAD + is a coenzyme involved in the redox reaction, which is necessary for converting the energy of nutrients into the human body's enzymes. It consists of two phosphate-linked nucleotides. One nucleotide contains adenine and the other is nicotinamide. It helps enzymes transfer electrons to ATP during redox reactions, which helps provide energy.
However, levels decrease with age-NAD + in older cells declines by more than 60%. If the level of NAD + increases, the intracellular energy mechanism may return to normal.
A team of scientists from the University of New South Wales and Harvard University found that this β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) can repair cell neurons. It also increases energy efficiency, and can even activate 'autophagy' (as mentioned in the 2016 Nobel Prize for cell autophagy). It's amazing and it's powerful.
Note: The above information is cited from below research, it does not represent the company's statement.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is transported into mammalian mitochondria
Antonio Davila, Ling Liu, Karthikeyani Chellappa, Philip Redpath, Eiko Nakamaru-Ogiso, Lauren M Paolella, Zhigang Zhang, Marie E Migaud, Joshua D Rabinowitz
Institute for Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, United States; University of Pennsylvania, United States;Princeton University, United States; Queen’s University Belfast, United Kingdom; Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, United States; Northeast Agricultural University, China; University of South Alabama, United States.
Function:
The NMN of "ReMage-power" can improve physical decline, lack of energy, metabolic disorders, poor sleep quality, and other symptoms.
For people:
People who feel low energy due to stress in work and life; People who work and live in environments with high levels of radiation or chemicals, such as flight attendants, scientists, and outdoor workers, and anyone who wants to keep skin healthy and young.
Dosage:
Take one capsule once a day before meals. Scientific studies confirm that the ingestion of NMN is safe and effective.
【Serving Size】600mg/60 capsules
【Shelf Life】3years
【Storage】Keep bottle closed and store at room temperature.
【Manufacturer】 Merion, Inc.
【Country of origin】 USA
【Warning】Not for pregnant and kid
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
参考文献
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is transported into mammalian mitochondria
Antonio Davila, Ling Liu, Karthikeyani Chellappa, Philip Redpath, Eiko Nakamaru-Ogiso, Lauren M Paolella, Zhigang Zhang, Marie E Migaud, Joshua D Rabinowitz
Institute for Diabetes, Obesity, and Metabolism, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, United States; University of Pennsylvania, United States;Princeton University, United States; Queen’s University Belfast, United Kingdom; Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, United States; Northeast Agricultural University, China; University of South Alabama, United States
Abstract
Mitochondrial NAD levels influence fuel selection, circadian rhythms, and cell survival under stress. It has alternately been argued that NAD in mammalian mitochondria arises from import of cytosolic nicotinamide (NAM), nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), or NAD itself. We provide evidence that murine and human mitochondria take up intact NAD. Isolated mitochondria preparations cannot make NAD from NAM, and while NAD is synthesized from NMN, it does not localize to the mitochondrial matrix or effectively support oxidative phosphorylation. Treating cells with nicotinamide riboside that is isotopically labeled on the nicotinamide and ribose moieties results in the appearance of doubly labeled NAD within mitochondria. Analogous experiments with doubly labeled nicotinic acid riboside (labeling cytosolic NAD without labeling NMN) demonstrate that NAD(H) is the imported species. Our results challenge the long-held view that the mitochondrial inner membrane is impermeable to pyridine nucleotides and suggest the existence of an unrecognized mammalian NAD (or NADH) transporter.
https://elifesciences.org/articles/33246
β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, an Anti-Aging Candidate Compound, Is Retained in the Body for Longer than Nicotinamide in Rats.
Kawamura T1, Mori N, Shibata K.
Abstract
The turnover of the oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) has attracted interest in regard to longevity. Thus, compounds that can rapidly increase the cellular NAD+ concentration have been surveyed by many researchers. Of those, β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (β-NMN) has been focused on. Studies on the biosynthesis of NAD+ from β-NMN have been reported at the cellular level, but not at the whole animal level. In the present study, we investigated whether β-NMN is superior to nicotinamide (Nam) as a precursor of NAD+ in whole animal experiments. To this end we compared the NAD+ concentration in the blood and the urinary excretion amounts of NAD+ catabolites. Rats were intraperitoneally injected with β-NMN or Nam. After the injection, blood samples and urine samples were collected at 3-h intervals. The concentration of blood total NAD (NAD11NADH) in each sample showed no significant differences between the two groups. The urinary excretion amounts of NAD+ catabolites in the urine samples collected at 3-6 h after the injection were lower in the β-NMN group than in the Nam group. These results suggest that β-NMN is retained in the body for longer than Nam.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27725413
Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice
Kathryn F. Mills,1 Shohei Yoshida,2 Liana R. Stein,1,§ Alessia Grozio,1 Shunsuke Kubota,3 Yo Sasaki,4Philip Redpath,5 Marie E. Migaud,5 Rajendra S. Apte,1,3 Koji Uchida,2 Jun Yoshino,6,* and Shin-ichiro Imai1,*
Summary
NAD+ availability decreases with age and in certain disease conditions. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), a key NAD+ intermediate, has been shown to enhance NAD+ biosynthesis and ameliorate various pathologies in mouse disease models. In this study, we conducted a 12 month-long NMN administration to regular chow-fed wild-type C57BL/6N mice during their normal aging. Orally administered NMN was quickly utilized to synthesize NAD+ in tissues. Remarkably, NMN effectively mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice. Without any obvious toxicity or deleterious effects, NMN suppressed age-associated body weight gain, enhanced energy metabolism, promoted physical activity, improved insulin sensitivity and plasma lipid profile, and ameliorated eye function and other pathophysiologies. Consistent with these phenotypes, NMN prevented age-associated gene expression changes in key metabolic organs and enhanced mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and mitonuclear protein imbalance in skeletal muscle. These effects of NMN highlight the preventive and therapeutic potential of NAD+
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5668137/
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide: Exploration of Diverse Therapeutic Applications of a Potential Molecule
Saikat Kumar Poddar 1,*,Ali Ehsan Sifat 1,Sanjana Haque 1,Noor Ahmed Nahid 1,Sabiha Chowdhury 1 andImtias Mehedi 2
1.Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Dhaka, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh
2.Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Dhaka, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh
Abstract
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a nucleotide that is most recognized for its role as an intermediate of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) biosynthesis. Although the biosynthetic pathway of NMN varies between eukaryote and prokaryote, two pathways are mainly followed in case of eukaryotic human—one is through the salvage pathway using nicotinamide while the other follows phosphorylation of nicotinamide riboside. Due to the unavailability of a suitable transporter, NMN enters inside the mammalian cell in the form of nicotinamide riboside followed by its subsequent conversion to NMN and NAD+. This particular molecule has demonstrated several beneficial pharmacological activities in preclinical studies, which suggest its potential therapeutic use. Mostly mediated by its involvement in NAD+ biosynthesis, the pharmacological activities of NMN include its role in cellular biochemical functions, cardioprotection, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and complications associated with obesity. The recent groundbreaking discovery of anti-ageing activities of this chemical moiety has added a valuable essence in the research involving this molecule. This review focuses on the biosynthesis of NMN in mammalian and prokaryotic cells and mechanism of absorption along with the reported pharmacological activities in murine model. View Full-Text
Keywords: ageing; Alzheimer’s disease; diabetes; ischemic preconditioning; nicotinamide mononucleotide; obesity
https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/9/1/34
More Information Dietary Supplement